How is malaria being transmitted?
We need a better understanding of which Anopheles mosquito species are transmitting malaria in different places, and how this is changing in response to interventions, urbanisation and climate change.
Where is insecticide resistance evolving and spreading?
Insecticide resistance is the biggest threat to our current tools for mosquito control. When resistance emerges, we need to identify and characterise it quickly, assess the risk, and track it as it spreads.
How can we move beyond control towards elimination?
Our current tools for mosquito control will only take us so far. We need to invent new ways to stop mosquitoes transmitting malaria, and be smart in how we use them.
The observatory is a collaborative effort to sequence the genomes of thousands of Anopheles mosquitoes and use those data to improve malaria control.
Anopheles gambiae complex
21,246 genomes from 32 countriesAnopheles funestus subgroup
3,964 genomes from 16 countriesAnopheles minimus
302 genomes from 1 countryTerms of use apply to some datasets within the observatory, but all data can be accessed and analysed for public health and educational purposes. See the data user guide for more information.



Video lectures in French or English and notebooks with executable code examples.
Study at your own pace, or enroll in an online course to learn alongside others with support from experienced teaching assistants.
API
Our cloud-native software for Python supports a range of functions for data access, visualisation, and statistical analysis.
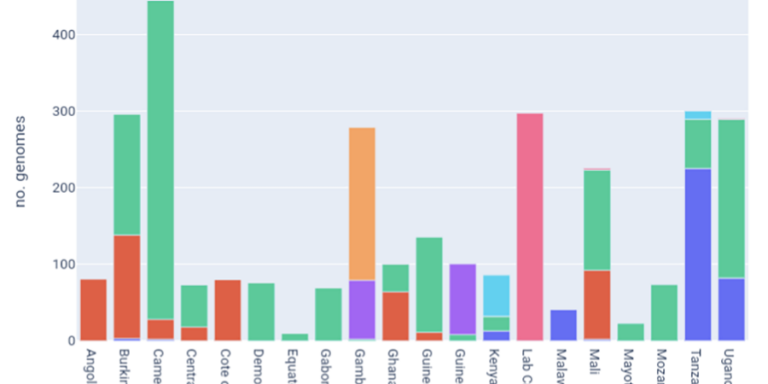
Explore available samples by country of origin, collection date and taxon.
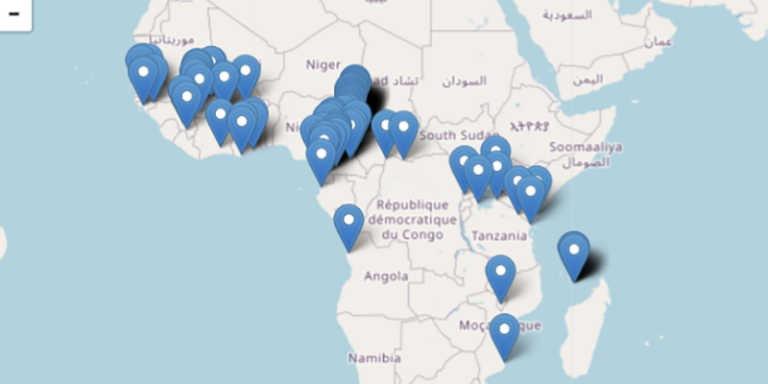
Explore available samples by collection location.
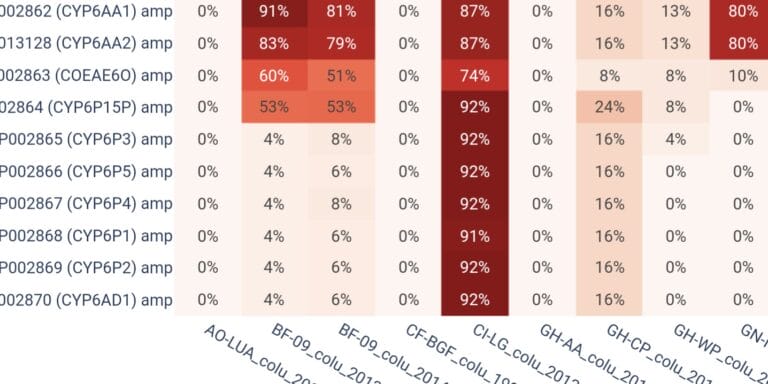
Compute frequencies of genetic variants in genes of interest.
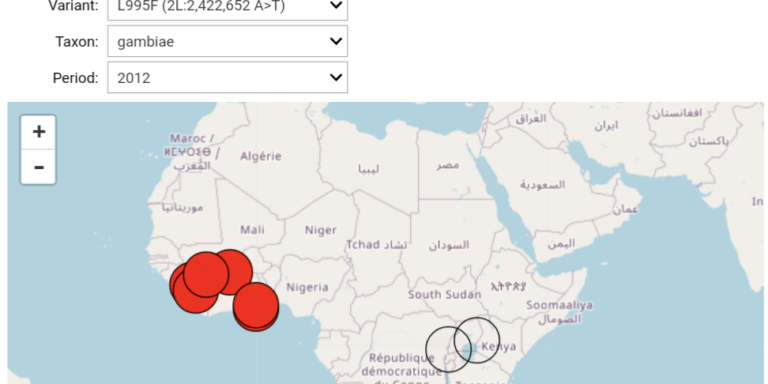
Compare the frequency of genetic variants between different geographical areas.
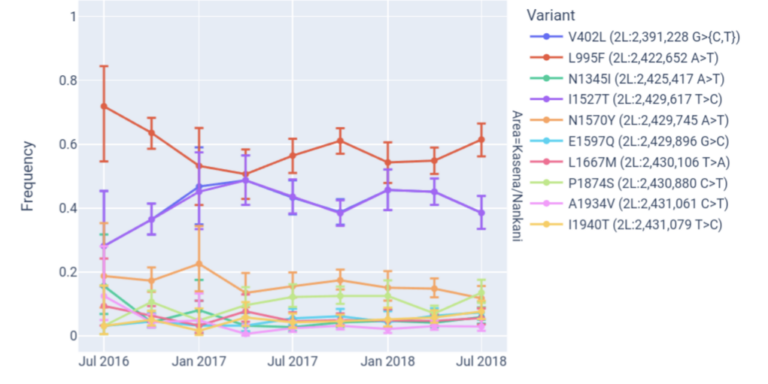
Analyse changes in variant frequencies over time.
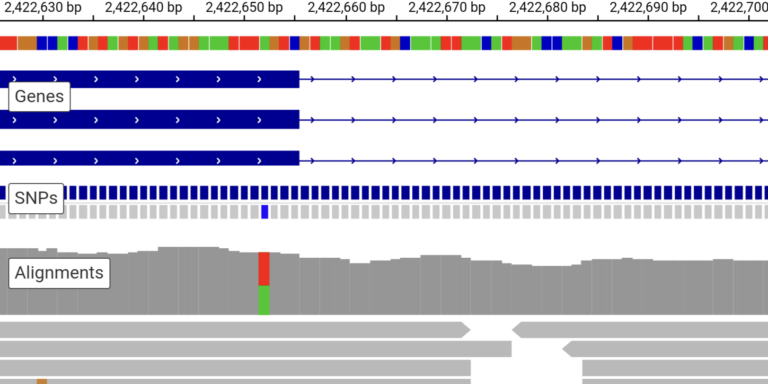
Browse sequence read alignments and assess the evidence for genetic variation in individual samples.
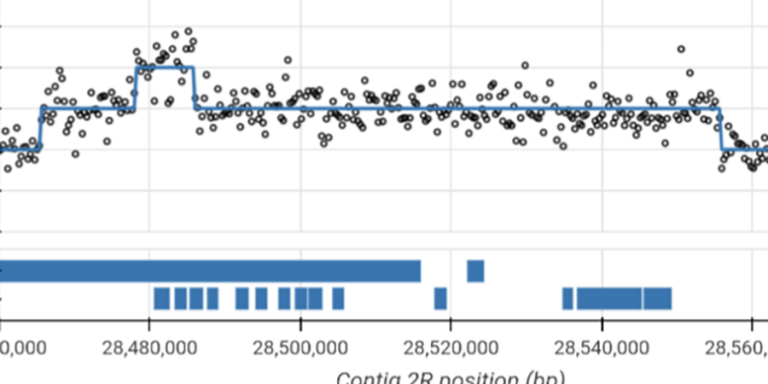
Visualise sequence read coverage and evidence for copy number variation in individual samples.
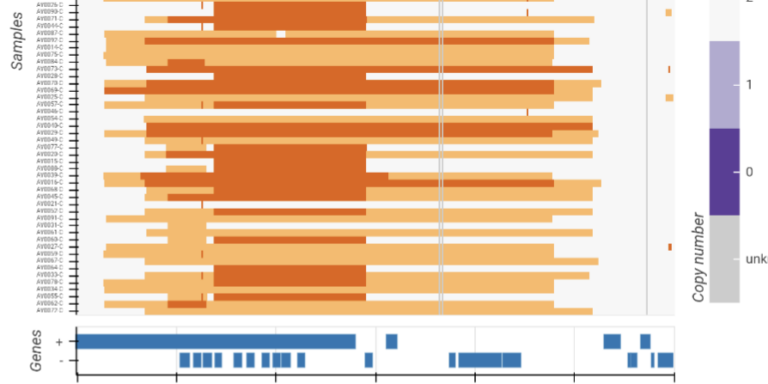
Visualise and compare copy number variation in multiple samples.
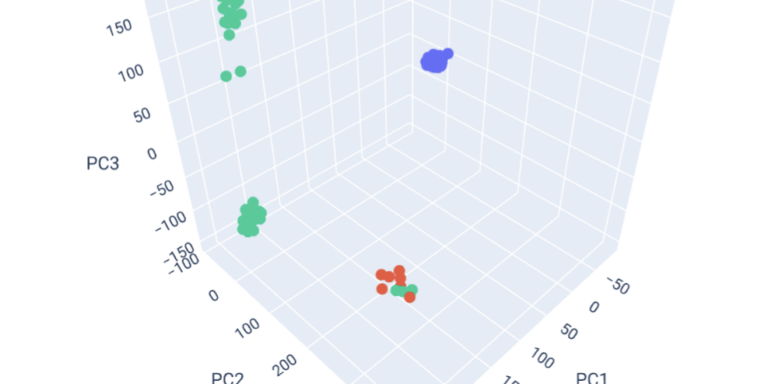
Explore population structure with principal components analysis.
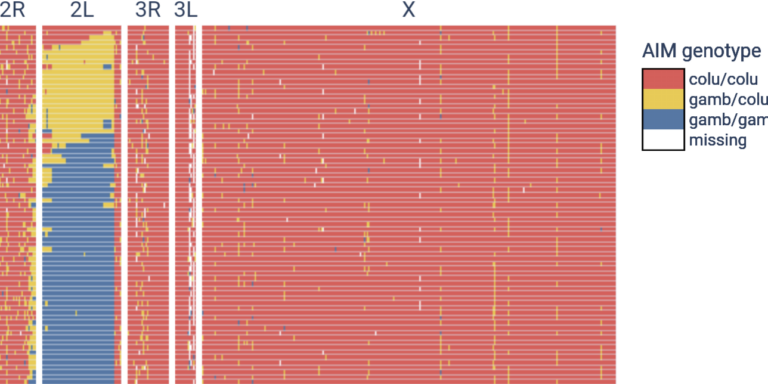
Investigate hybridisation and introgression between species with ancestry-informative markers.
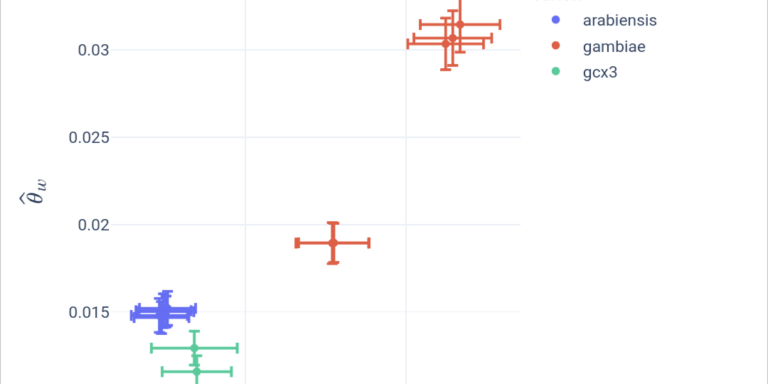
Quantify and compare genetic diversity between populations.
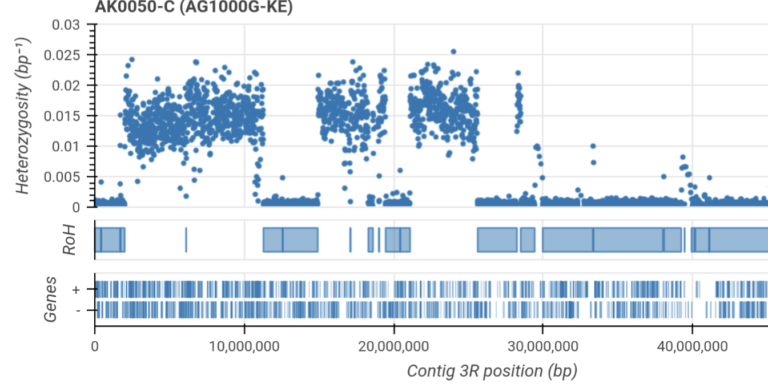
Infer runs of homozygosity and investigate evidence for inbreeding.
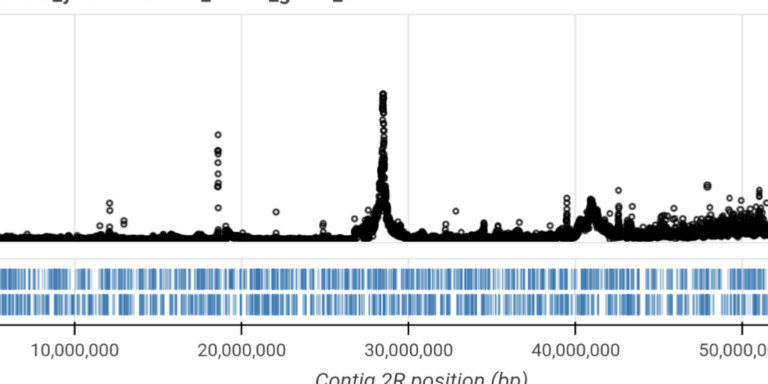
Perform genome-wide selection scans to discover new resistance genes.
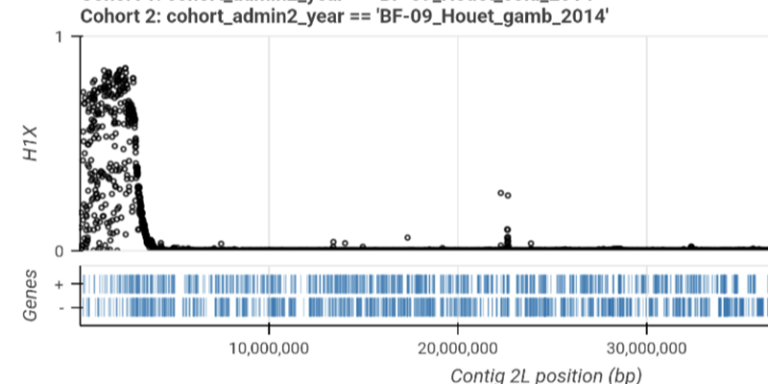
Find genes where adaptive gene flow is occurring between countries or species.
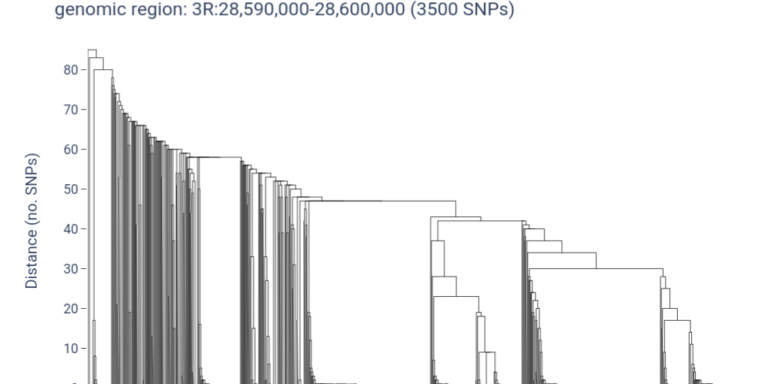
Use haplotype clustering to investigate selective sweeps and gene flow within a gene of interest.
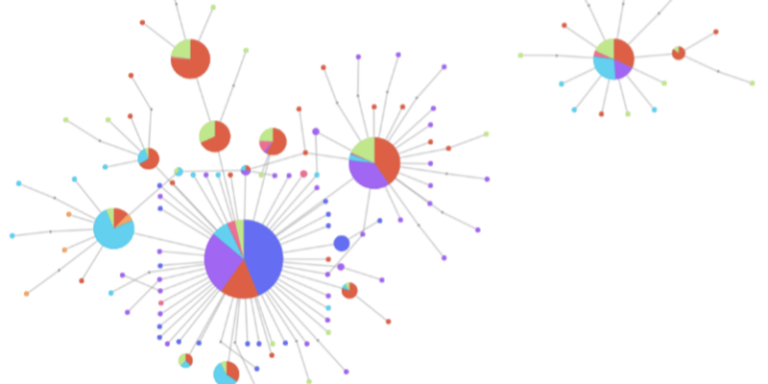
Use haplotype networks to explore selective sweeps and gene flow within a gene of interest.
Google Colab
Colab is an interactive computing service provided for free by Google Research and is ideal for exploratory analyses.MalariaGEN Datalab
The Genomic Surveillance Unit at the Sanger Institute hosts a JupyterHub service running in Google Cloud that is available for free to observatory partners for more intensive analyses.Terra
Terra is a cloud platform for biomedical research supporting workflows and interactive notebooks, and can be used for a wide range of analyses.Alternatively, observatory data can be downloaded to your own compute resources to run analyses locally.
Research
The observatory is powering new research into the biology and control of malaria vectors.