Introduction
The P. falciparum Genetic Crosses project is generating high-quality data on genome sequence variation and sexual recombination for the parents and progeny of parasite crosses.
Objectives & Coordination
Discovering the genetic causes of natural phenotypic variation in P. falciparum requires a combination of epidemiological and laboratory-based approaches. A powerful laboratory approach, which was instrumental in discovering the chloroquine resistance gene PfCRT, involves crossing two parasite strains with different phenotypic characteristics and then studying the resulting progeny.
Unfortunately, it is extremely laborious to perform genetic crosses for P. falciparum, and to date it has been accomplished only four times. The strains that have been crossed are 3D7 with HB3 (Walliker et al, 1987), HB3 with Dd2 (Wellems et al, 1990) and 7G8 with GB4 (Hayton et al, 2008). A fourth cross between clones 803 and GB4 was recently performed to study the genetic basis for artemisinin resistance. The parents and progeny of these genetic crosses represent a hugely valuable resource for the malaria research community to investigate a range of different phenotypes.
Assembling a complete and accurate picture of P. falciparum genome variation from short sequence reads presents many analytical challenges, particularly in regions of the genome that are highly polymorphic or made up of repetitive elements. To provide researchers with data resources to help overcome these challenges, the P. falciparum Genetic Crosses project has:
- Sequenced the parents and 78 progeny clones from the crosses 3D7xHB3, HB3xDd2 and 7G8xGB4
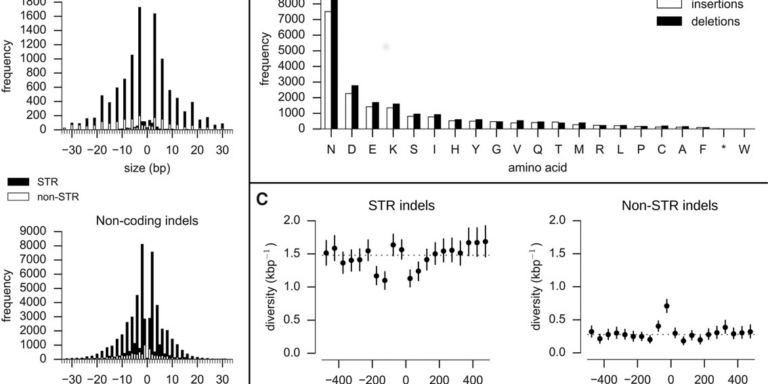
- Performed the first integrated analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), INDELs and complex polymorphisms in P. falciparum, using Mendelian error rates as an indicator of genotypic accuracy
- Released sequence data and variant calls open access, and provided a dedicated web application to increase the usefulness of these data resources
Data
Data generated by the P. falciparum Genetic Crosses project is made available open access.
Current
Sample set: Parents and 78 progeny clones from three crosses (3D7xHB3, HB3xDd2 and 7G8xGB4)
Sequence data and variant calls
Open access
Partner studies
Performing crosses of two parasite strains with different phenotypic characteristics and then studying the resulting progeny is a fruitful method of exploring some of the genetic mechanisms underpinning these phenotypes. Genetic crosses also…
Performing crosses of two parasite strains with different phenotypic characteristics and then studying the resulting progeny is a fruitful method of exploring some of the genetic mechanisms underpinning these phenotypes. Genetic crosses also…
Performing crosses of two parasite strains with different phenotypic characteristics and then studying the resulting progeny is a fruitful method of exploring some of the genetic mechanisms underpinning these phenotypes. Genetic crosses also…
Publications
- Indels, structural variation, and recombination drive genomic diversity in Plasmodium falciparum
Miles et al.Genome Research, 2016; 26 1288-1299
98 samples
from
3 crosses
Project contact
People
The following investigators are involved in the P. falciparum Crosses project.
Updates
18 Aug 2015
Manuscript on bioRxiv
A preprint of a manuscript highlighting several interesting features of the genetic crosses data (v1.0) is now available on bioRxiv. This manuscript reports findings from an integrated analysis of SNP, INDEL and complex polymorphisms in both coding and non-coding regions of the core genome. The paper also explores meiotic recombination, estimating rates of crossover and non-crossover recombination, and describing recombination events that affest drug resistance genes mdr1 and gch1.
18 Aug 2015
Public release of P. falciparum genetic crosses data (v1.0)
We’ve publicly released a new data resource (v1.0) including whole-genome sequence and genetic variation data from the parents and offspring of three parasite crosses. Read more about this data release.